top of page


Respiratory disorders in chicks and hens
Respiratory disorders in chicks and hens are a common issue and should not be underestimated – sometimes it is “just” environmental conditions, and sometimes a serious infectious disease. Common Signs • Open-mouth breathing / gasping • Wheezing, snorting, “clicking” • Runny nose, discharge from the nose or eyes • Sneezing, coughing • Swelling in the face / around the eyes • Decreased eating, weakness, slowed growth • In chicks – sudden death
4 days ago1 min read


Respiratory disorders in cows and calves
Respiratory disorders in cows and calves are a common phenomenon in dairy farms, especially in young calves. The causes can be divided into several main groups, with different emphases for calves versus mature cows: Infectious agents (most common) Viruses • IBR (infectious herpes) – cough, runny nose, fever, shortness of breath • BRSV – acute shortness of breath, open mouth breathing, sometimes sudden death • PI3 – mild-moderate illness, sometimes preparation for
Jan 202 min read


The digestive system in sheep and goats
Digestive problems in sheep and goats are very common, and can result from nutrition, parasites, infections, or poor management. Below is an organized overview by main groups – with signs, causes, and treatment/prevention directions: Stomach and Rumen Problems 1. Bloat Symptoms: • Swollen left abdomen • Restlessness, difficulty breathing • Not eating Causes: • A sharp transition to green fodder/legumes • High concentration of grains • Esophageal ob
Jan 161 min read


Digestive problems in horses
Digestive problems in horses are among the most common causes of morbidity and even mortality, due to the high sensitivity of their digestive systems. I will list them from common to dangerous, with main signs and causes: Colic – the most important A general name for abdominal pain, with many subtypes: Common types: • Gas colic – gas buildup due to diet/food change • Constipation colic – lack of water, insufficient fiber • Sand colic – eating on sandy ground...
Jan 121 min read


Digestive system problems in calves and cows
Digestive system problems in calves and cows are very common, but the causes and clinical manifestations differ between a young calf and an adult cow. I will arrange them according to age and type of problem. Calves – Common Digestive Problems 1. Calf Diarrhea The most common problem • Infectious agents: • E. coli • Rotavirus / Coronavirus • Cryptosporidium • Salmonella • Nutritional factors: • Poor quality/insufficient quantity of col
Jan 82 min read


Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders in sheep and goats
A systematic clinical-veterinary review of skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders in sheep and goats, according to groups of factors - with emphasis on field diagnosis and prevention: Infectious Diseases 1. Sheep & Goat Pox • Cause: Virus • Signs: Nodules → Blisters → Scabs, Fever, Decreased Eating • Common Location: Face, Udder, Genital Area • Importance: Highly Contagious, Sometimes Fatal • Prevention: Vaccination, Isolation 2. Orf (Orf – Ecthyma contag
Jan 52 min read


Congenital diseases in cows and cattle
Main causes of congenital diseases • Genetics / Heredity – latent carriers, close matings • Infections during pregnancy – mainly viral • Nutritional deficiencies in the pregnant cow (vitamins, minerals) • Toxins and medications during pregnancy • Damage to fetal develo pment in early pregnancy Nervous system • Hydranencephaly – partial/complete absence of the brain Related to BVD, Schmallenberg • Cerebellar hypoplasia – underdevelopment of th
Jan 11 min read


Congenital diseases in chickens
Common diseases and birth defects in chickens, especially in chicks and young chickens: Skeletal defects • Leg deformities – bowed legs, splay legs, shortened tendons • Crooked toes – usually related to vitamin deficiencies (especially B2) or genetics • Spinal curvature/deformity – kyphosis / scoliosis • Lack of wings / shortened wings Neurological defects • Head tremors and lack of coordination • Congenital paralysis • Head tilt Sometimes relat
Dec 26, 20251 min read


Congenital diseases in horses
Congenital diseases and defects in horses are conditions that are present at birth, usually due to genetics, but sometimes also due to conditions during pregnancy (infections, poor nutrition, toxins). Below is an overview arranged by body system: Musculoskeletal System Angular Limb Deformities (ALD) Limb deformities – legs curved in/out. Common in foals. Flexural Deformities (Contracted Tendons) Excessive bending of joints (e.g. “club foot”). Dwarfism Rare, usually genetic, w
Dec 20, 20252 min read


Eyeball conditions in sheep and goats
Common eye conditions in sheep and goats 1) Keratitis – inflammation of the cornea What you see: • White/blue cloudiness of the cornea • Sensitivity to light • Lacrimation • Sometimes fine blood vessels penetrate the cornea Common causes: Injury, foreign body, bacterial infection, or virus (mainly IBR-like in goats). 2) Corneal Ulcer What you see: • White/gray spot on the cornea • Closed eye • Significant pain • May progress quickly and
Dec 11, 20252 min read


Conditions of the conjunctival area in young sheep and goats
Common Conjunctival Conditions in Young Sheep and Goats 1) Conjunctivitis – Bacterial Common Causes: • Mycoplasma conjunctivae – a major cause in herds • Chlamydophila pecorum • Moraxella bacteria (less common than in cattle) Signs: • Redness of the conjunctiva • Profuse tearing • Swelling of the eyelids • Sensitivity to light (photophobia) • Small blisters may appear on the conjunctiva Treatment: • Ophthalmic antibiotics (tetracycline) •
Dec 8, 20252 min read

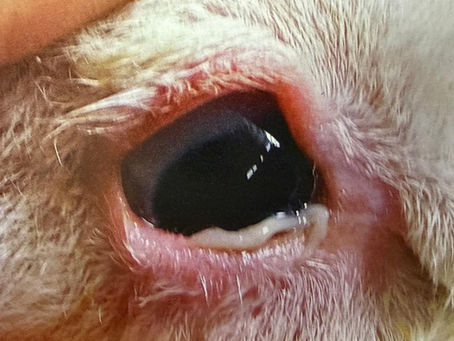
Periocular disorders of the eyelid and conjunctiva in young sheep and goats
Eyelid and Conjunctival Disorders in Young Sheep and Goats The eye of a sheep/goat is very susceptible to infections, irritations and parasites. At a young age the immune system is weaker and therefore problems are more common. 1) Conjunctivitis Common causes • Bacteria – Chlamydia pecorum, Mycoplasma spp., Moraxella ovis • Viruses – usually as part of a respiratory illness • Environmental irritation – dust, strong wind, ammonia in the barn • Trauma – scratche
Dec 5, 20252 min read


Eye disorders in young sheep and goats
1) Infectious Keratoconjunctivitis (Pinkie Pie) The most common cause. Causes: • Mycoplasma conjunctivae • Chlamydophila pecorum • Sometimes Moraxella or other Mycoplasma bacteria Signs: • Very watery eyes • Redness of the conjunctiva • Light sensitivity (photophobia) • Corneal cloudiness • Calf/lamb standing with eye half-closed • Sometimes bulging adhesions Treatment: • Topical antibiotics: drops/ointment containing tetracycline
Dec 1, 20252 min read


Spinal cord problems in sheep and goats
Spinal Cord Problems in Sheep and Goats Diseases and injuries to the spinal cord are more common than you might think, and can cause paralysis, weakness, difficulty walking, and changes in posture. 1. Trauma and external injuries Causes: • Kicking between animals • Falls • Injuries from pressure or trampling • Entanglement in fences Signs: • Sudden posterior paralysis • Inability to stand • Severe pain in the spine • Poor or absent reflexes
Nov 28, 20252 min read


Cranial nerve disorders in sheep and goats
Cranial nerve disorders in sheep and goats are most often caused by infectious diseases, trauma, toxicity, or nutritional problems. The damage can be to a single nerve or to multiple nerves together. 1. Infectious diseases that cause damage to the cranial nerves A. Listeriosis (Listeria monocytogenes) – most common • Infection of the brainstem → damage to nerves III–XII. • Typical signs: • Head tilt (torticollis) • Facial paralysis (nerve VII) – drooping ear, open eye
Nov 25, 20252 min read


Intracranial lesions in the central nervous system in sheep and goats
Intracranial lesions in sheep and goats The term “intracranial lesions” refers to any injury, inflammatory process, mass, or damage located within the skull—that is, in the brain, meninges, or cerebral blood vessels. These lesions often cause significant neurological disorders due to pressure on sensitive tissues or direct impairment of their function. Types of Central Intracranial Lesions 1) Brain Infections and Infections (Encephalitis / Meningitis) Those that cause the for
Nov 21, 20252 min read


Nervous system disorders in young sheep and goats
1. Clostridial encephalitis (Clostridium perfringens Type D) What is it: A toxin that damages the brain, most common in lambs and kids with a sharp increase in food intake. Symptoms: Unsteady gait Tremors Twitches Seizures Rapid death Prevention: Clostridia vaccine (Abisol/Clostridium 7–8 WAY) Gradual transition to a rich food 2. Listeriosis (Listeria monocytogenes) – inflammation of the brain and brainstem More common in adults but also occurs in young people. Typical sympto
Nov 16, 20252 min read

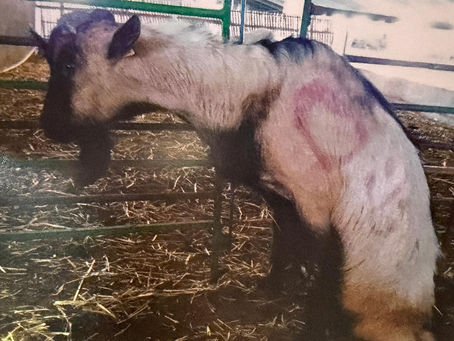
Neurological disorders in sheep and goats
Neurological disorders in sheep and goats (neurological = of the nervous system) are a broad group of diseases and injuries that affect the brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves or muscles. They can cause changes in behavior, gait, balance and response to stimuli. Here is an overview of the main disorders: 1. Listeriosis Cause: Listeria monocytogenes. Main cause: Consumption of spoiled feed (usually too acidic silage). Clinical signs: Turning the head to one side, walking in
Nov 14, 20252 min read

Foot disorders in sheep and goats
Foot disorders in sheep and goats are very common problems, especially in herds that graze in wet, muddy or heavily soiled conditions. They can cause lameness, pain, decreased appetite, reduced milk yield and fertility. Here is a quick overview of the main disorders: 1. Foot Rot (Fusiformis necrophorum + Dichelobacter nodosus) Cause: Anaerobic bacteria. Favorable conditions: dampness, mud, poor hygiene, injuries to the hoof. Clinical signs: Pungent odor and rot in the hoof De
Nov 10, 20252 min read


Disorders originating in the bones, joints and tendons in sheep and goats
Bone Disorders 1. Rickets and Osteomalacia Caused by a deficiency of vitamin D, calcium, or phosphorus. In young lambs and kids, rickets occurs: soft bones, bowed legs, lameness, and growth retardation. In adults — osteomalacia: brittle bones, weakness, and sometimes deformity of the pelvic bones and vertebrae. 2. Fractures Result from trauma — falls, running over, or assault. Seems like sudden lameness, swelling, pain, and sometimes abnormal movement of the limb. 3. Osteomye
Nov 6, 20252 min read
bottom of page
